Dr. Sanjeev K. Khulbey
Heart attack, very commonly used words in our day to day life has great impact on physical, financial and mental health of our society. Actually heart attack is sequelae of coronary artery disease. Coronary arteries are main source of nutrition and oxygen for our heart which works continuously through out day and night.
We have two coronary artery right and left which supplies the heart muscles with different branches. Any factor which results in hardening and narrowing of these arteries result in heart attack or Myocardial infarction.
WHAT CAUSES CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE ?
Coronary artery disease occurs due to hardening of coronaries which is the result of deposition of atherosclerotic plaque. This plaque is primarily made up of cholesterol. The accumulation of plaque depends on multiple factors. These are called risk factors for coronary artery disease.

These risk factors are categorised in modifiable and non modifiable category. Non modifiable factors are advance age, gender, race etc. Modifiable risk factors are smoking, Diabetes, Hypertension, obesity and stress etc. We can control the risk factors as primary and secondary level prevention.
WHAT ARE SYMPTOMS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE ?
- The symptoms are variable in coronary artery disease. Symptoms are chest pain (angina), often associated with exertion, radiating to hand, neck and jaw.
- Some patients especially diabetics or patients with kidney disease may not have any symptoms (silent MI).
- The patients with significant narrowing nay present as rest pain in the chest (Unstable angina).
- Some patients may present with shortness of breath with or with out chest pain.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE ?
Heart attack can be diagnosed with cardiac enzymes, namely Trop I, Trop T,CPK-MB.
ECG (EKG) is an important test in determining Coronary artery disease and heart attack. Any changes in ECG suggest detail cardiac evaluation.
When resting ECG is normal in high risk category patient stress ECG or TMT is advised. TMT has 60 to 70% accuracy in determining heart disease.
When patient is not able to perform TMT, stress Echo or Thallium scan is helpful in assessing coronary artery disease. The accuracy of these is 80 to 90 %. In this artificial stress is created with the help of medicines and nuclear dye is injected.
An area of heart with normal blood at rest and reduced blood flow during exercise signifies coronary artery disease. Similarly in stress Echo area of reduced movement is identified to diagnose coronary artery disease.

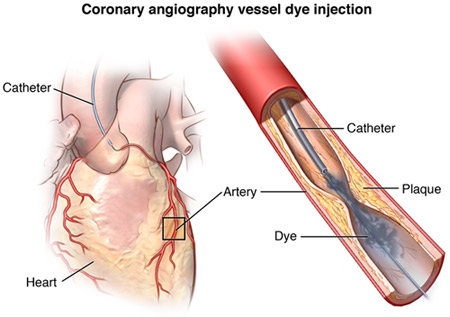
Coronary angiography is the gold standard for diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease. It not only helps in identifying site of blockage but also helps in planning of treatment. CT Coronary angiogram or Cardiac CT is the new modality for diagnosing coronary artery disease. It gives detail picture of coronary anatomy and blockages.
HOW TO TREAT CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE ?
The most important measure in treatment of coronary artery disease is life style modification. Avoid smoking, healthy food, good sleep, control weight, avoid stress and exercise are few important points to adapt.Medicines has important role in controlling heart disease.
Coronary artery disease is a lifestyle related progressive disease. Different medications helps in controlling progression of disease. Medicines includes anti diabetics, antihypertensive, statins(lowers choleterol), antianginal, dilators, diuretics and blood thinners.
Definitive management for coronary artery disease is coronary revascularisation. There are two widely accepted and scientifically proved methods. These are percutaneous coronary angioplasty (PTCA) and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). In current situation CABG is accepted as better method in various sets of disease.
HOW IS PTCA STENTING DONE ?
This is relatively less invasive method of revascularisation. The long term outcomes depends on many factors like presence of Diabetes, site and size of stenosis etc. In this a catheter is passed from groin or hand in to the heart. This is passed across the stenosis.
Just at the site of blockage PTCA balloon is inflated and stent is deployed. The inflated condition of stent allows normal flow across the coronary artery. The patient needs to be hospitalised for 4 to 5 days and discharged with medicines.
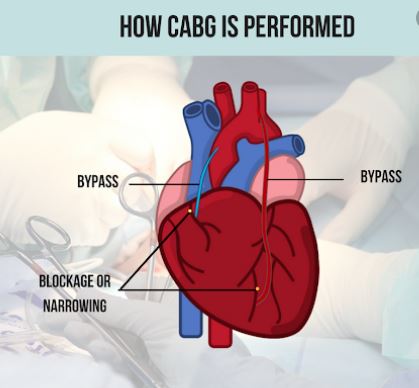
HOW IS CABG DONE ?
This procedure envolves detail evaluation followed by surgery. Surgery is usually performed by cutting chest bone(sternum). Other methods are minimal invasive or robot assisted CABG which is performed by cutting between the ribs {thoracotomy}.
The surgery is performed on beating heart (OFF pump CABG) and on cardiopulmonary bypass(On pump CABG). In this a conduit or graft is placed distal to the disease or stenosed segment of coronary artery.
The conduits commonly used are Internal mammary artery from chest wall, Radial artery from hand and Saphaneous vein from leg. The patient needs to be hospitalised for 7 to 10 days for this surgery. The CABG surgery has best long term results in terms of symptom relief and quality of life.
 Jubilee Post News & Views
Jubilee Post News & Views